Dharmamitra.org AI application for classical Asian Languages
Dharmamitra is a website that provides state-of-the-art machine translation and semantic search functionality for the classical Asian languages Sanskrit, Pali, Tibetan, and Chinese.
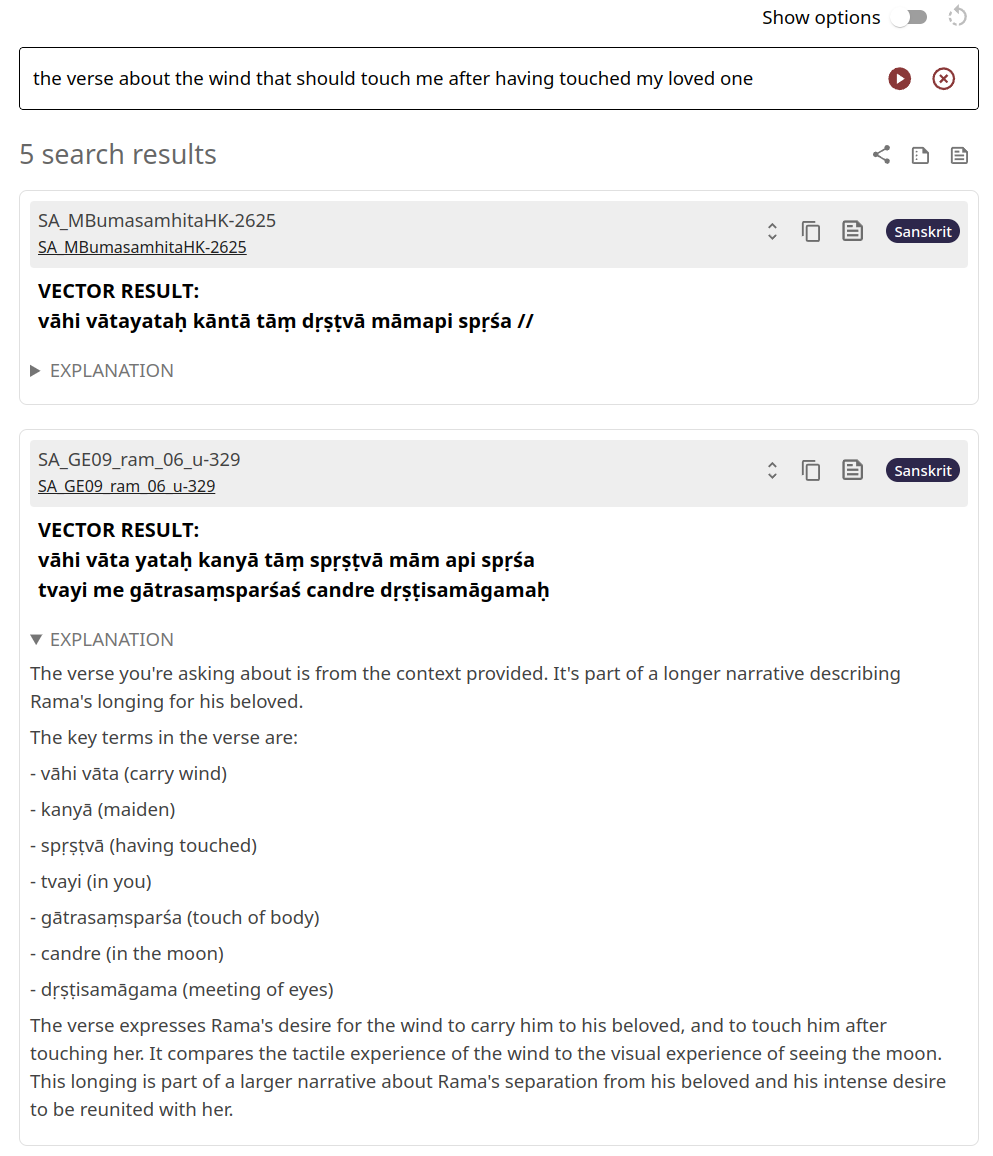
Dharmamitra is a website that provides state-of-the-art machine translation and semantic search functionality for the classical Asian languages Sanskrit, Pali, Tibetan, and Chinese.

Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Published in Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2018
This paper presents end-to-end neural network models for Sanskrit tokenization, jointly handling compound splitting and Sandhi resolution. The language-agnostic models outperform previous approaches for Sanskrit and also excel in German compound splitting.
Recommended citation: Hellwig, O., & Nehrdich, S. (2018). "Sanskrit Word Segmentation Using Character-level Recurrent and Convolutional Neural Networks." In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP).
Download Paper
Published in Journal of the Japanese Association for Digital Humanities, 2020
This paper introduces a novel approach to detect parallel passages in the Chinese Buddhist canon using continuous word representations and nearest neighbor search. It evaluates the quality of detected parallels and demonstrates a web application for philological research.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S. (2020). "A Method for the Calculation of Parallel Passages for Buddhist Chinese Sources Based on Million-scale Nearest Neighbor Search." Journal of the Japanese Association for Digital Humanities, 5(2), 132-153.
Download Paper
Published in CHR 2021: Computational Humanities Research Conference, 2021
This paper introduces a latent variable model for ancient languages to quantify the influence of early authoritative works on their literary successors in terms of lexis. The model jointly estimates word reuse and composition dates, applied to a corpus of pre-Renaissance Latin texts.
Recommended citation: Hellwig, O., Sellmer, S., & Nehrdich, S. (2021). "Obtaining More Expressive Corpus Distributions for Standardized Ancient Languages." In Proceedings of the Computational Humanities Research Conference (CHR 2021), Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Download Paper
Published in Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Language Technologies for Historical and Ancient Languages, 2022
This paper explores the use of Latin BERT word embeddings for morpho-syntactic tagging and introduces a graph-based dependency parser for Latin. The proposed models show competitive performance in tagging and outperform various baselines in parsing.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S., & Hellwig, O. (2022). "Accurate Dependency Parsing and Tagging of Latin." In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Language Technologies for Historical and Ancient Languages, pages 20-25, Marseille, France. European Language Resources Association.
Download Paper
Published in Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, 2022
This paper introduces SansTib, a large-scale Sanskrit-Classical Tibetan parallel corpus with 317,289 automatically aligned sentence pairs. It also presents a bilingual sentence embedding model and evaluates the quality of the automatic alignment using a gold evaluation dataset.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S. (2022). "SansTib, a Sanskrit - Tibetan Parallel Corpus and Bilingual Sentence Embedding Model." In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, pages 6728-6734, Marseille, France. European Language Resources Association.
Download Paper
Published in Language Resources and Evaluation, 2023
This paper introduces the first data-driven parser for Vedic Sanskrit, exploring various input feature representations and analyzing parsing errors. The optimal model achieves 87.61 unlabeled and 81.84 labeled attachment scores, demonstrating good performance for this under-resourced ancient Indo-Aryan language.
Recommended citation: Hellwig, O., Nehrdich, S., & Sellmer, S. (2023). "Data-driven dependency parsing of Vedic Sanskrit." Language Resources and Evaluation, 57, 1173-1206.
Download Paper
Published in NLP4DH, 2023
This paper presents a novel dataset and fine-tuned models for machine translation of Buddhist Classical Chinese, outperforming commercial solutions in efficiency and performance.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S., Bingenheimer, M., Brody, J., & Keutzer, K. (2023). "MITRA-zh: An efficient, open machine translation solution for Buddhist Chinese." NLP4DH.
Download Paper
Published in Religions, 2023
This study applies computer-aided methods to detect textual reuse in Xuanzang’s translation corpus and selected Abhidharma texts in Chinese. It presents network graph visualizations and examines reuse patterns, demonstrating alignment with established scholarship and providing a foundation for future detailed studies.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S. (2023). "Observations on the Intertextuality of Selected Abhidharma Texts Preserved in Chinese Translation." Religions, 14(7), 911.
Download Paper
Published in The 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (Findings), 2024
This paper introduces ByT5-Sanskrit, a new pretrained language model for Sanskrit NLP tasks, demonstrating superior performance in word segmentation, dependency parsing, and OCR post-correction, while also introducing a novel multitask dataset.
Recommended citation: Nehrdich, S., Hellwig, O., & Keutzer, K. (2024). "One Model is All You Need: ByT5-Sanskrit, a Unified Model for Sanskrit NLP Tasks." In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (Findings).
Download Paper
Published in Revue d'Etudes Tibétaines, 2024
This paper discusses recent advancements in Tibetan Natural Language Processing and Digital Humanities.
Recommended citation: Meelen, M., Nehrdich, S., & Keutzer, K. (2024). "Breakthroughs in Tibetan NLP & Digital Humanities." Revue d'Etudes Tibétaines. 72, 5-25.
Download Paper
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Translation and search are among the fundamental problems when researching the textual source material of Buddhist traditions. MITRA has successfully developed machine translation models to ease the access to this material. When it comes to search, The Dharmamitra project approaches this problem by using semantic embeddings that enable search on related passages in different languages, regardless of whether the answer to the query is found in a text preserved in Pāli, Sanskrit, Tibetan, or Chinese. In addition to providing researchers with this powerful search system, Dharmamitra also provides a system for the automatic detection of similar text passages within the same language and across different languages. In my talk, I will demonstrate how these tools are designed and how researchers can access them and integrate them in their workflow.
Published:
Recent years saw the rise of multilingual language models that achieve high levels of performance for a large number of tasks, with some of them handling hundreds of languages at once. Premodern languages are usually underrepresented in such models, leading to poor performance in downstream applications. The Dharmamitra project aims to develop a diverse set of language models to address these shortcomings for the classical Asian low-resource languages Sanskrit, Tibetan, Classical Chinese, and Pali. These models provide solutions for low-level NLP tasks such as word segmentation and morpho-syntactic tagging, as well as high-level tasks including semantic search, machine translation, and general chatbot interaction. The talk will address the individual challenges and unique characteristics of the data involved, and the strategies deployed to address these. It will also demonstrate how these different tools can be combined in an application that goes beyond simple sentence-to-sentence machine translation, providing detailed grammatical explanations and corpus-wide search to support both early-stage language learners and experienced researchers with specific demands.
Published:
Published:
This talk was presented as part of the workshop “Case studies from current research projects - Conversations on Digital Scholarly Editing” organized by Martina Dello Buono and Florinda De Simini at L’Orientale University of Naples.
Published:
Part of the International Symposium “Buddhist Studies and Digital Humanities: 100 Years of the Taishō Tripiṭaka and 30 Years of SAT”
Published:
Recent advances in artificial intelligence and natural language processing have revolutionized information retrieval and question-answering systems. This talk introduces MITRASearch, a specialized search platform designed for exploring Buddhist literature preserved across Classical Asian languages including Chinese, Tibetan, Sanskrit, and Pāli. The system leverages multilingual approximate search capabilities to enable scholars to identify parallel passages and conduct comparative analyses across different writing systems and translations. We demonstrate how large language models integrated into the Dharmamitra project enhance user interaction with search results, facilitating dynamic exploration of these classical texts. This innovation addresses the long-standing challenge of cross-linguistic textual research in Buddhist studies and offers new possibilities for digital humanities scholarship.
Published:
With the advent of large language models, machine translation (MT) has become a widely used, but little understood, tool for research, language learning, and communication. GPT, Claude, and many other model series allow researchers now to access literature in different languages, and even translate primary texts composed in classical languages with few resources available. But how to evaluate the translation output of such machines? How to decide which model is the best for my own research purposes and how to tweak it? How will MT impact language learning, which is fundamental for Asian Studies?
Published:
This presentation was part of a workshop at Keio University, co-organized by Kakenhi Special Promotion Research “Compilation of the Reiwa Daizokyo as a Digital Research Infrastructure - Presentation of a Research Infrastructure Construction Model for Next-Generation Humanities (JP25H00001)” and the Research Infrastructure Hub, Research and Development Project for the DX of Humanities and Social Sciences.
Published:
This presentation is part of an online workshop on digital approaches to intertextuality in pre-modern East Asian texts. The talk will provide a preliminary investigation of different representation methods for semantic similarity tasks in Buddhist Chinese and related languages of the Buddhist tradition.
Published:
Traditional philological work on Buddhist sources often consists of laborious keyword searches across disparate corpora in multiple languages, followed by manual collation of parallels, a workflow that favours stamina over insight. Dharmamitra is an open-source platform that collapses those tasks to seconds using advanced computational and deep learning methods.
Published:
Recent advances in machine learning, particularly the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, are rapidly shaping new ways of accessing and interpreting knowledge preserved in textual form. This has far-reaching implications for the study of the Buddhist textual tradition. Applications once considered decades away, such as the fluent machine translation of Classical Tibetan or Chinese into English, are now commonly used by scholars at all levels, from early-career students to senior researchers. This talk will provide an overview of the tools that the Dharmamitra project currently offers the Buddhist Studies community, with a focus on machine translation and cross-lingual search for philological use cases. It will also introduce the underlying technical architecture of these tools and discuss both the capabilities and limitations of the current generation of language models for philological applications.
Published:
I presented as part of the Digital Archive Research Unit at the Center for Integrated Japanese Studies (CIJS) at Tohoku University. The workshop and symposium was co-hosted by CIJS, the Tohoku University Digital Archives Steering Committee, and the Tohoku University Library. I delivered a lecture and participated in a panel discussion on the digitization of academic resources in Tohoku University and new developments in Buddhist textual studies with AI technology.
Published:
I presented on the Dharmamitra platform as part of the panel “AI in the Fo Guang Dictionary of Buddhism English Translation Project and MITRA.” The panel showcased how emerging AI tools support large-scale Buddhist translation and lexicographical research. I introduced Dharmamitra as a collaborative AI-driven platform developed by Tohoku University with the Tsadra Foundation and Berkeley AI Research Lab, which employs Large Language Models for high-quality machine translation of Sanskrit, Pali, Tibetan, and Chinese alongside vector-based semantic retrieval.
Published:
I presented on the current status and future outlook of the Dharmamitra ecosystem, covering translation, OCR, and semantic retrieval capabilities for Buddhist texts. The symposium was held at Tokyo International Forum Hall D5 and focused on “The Significance of Humanities and Research Infrastructure Development in the DX-AI Era.”
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.